 |
 |
| Korean J Med > Volume 80(3); 2011 > Article |
|
요약
방법:
부산 및 울산의 7개 3차 병원에서 처음 고혈압을 진단받고 외래진료를 받은 20세 이상의 성인을 대상으로 하였고, 기존에 고혈압 약제를 복용하고 있었던 환자는 최초 진료 당시 혈압이 조절되지 않아 기존 약제에서 치료내용이 변경된 경우 연구대상에 포함하였다. 2003년 개정된 세계 보건기구/국제 고혈압학회(World Health Organization/International Society of Hypertension, WHO/ISH) 기준에 따라 후향적 의무기록 분석을 통해 위험도를 층별화 하였다.
결과:
총 643명이 분석 대상에 포함되었다. 전환효소 차단제 혹은 안지오텐신 II 수용체 차단제가 가장 빈번하게 처방되고 있었다. 최초 처방시점과 치료 1년째에 더 높은 위험도 군일수록 처방 받는 항고혈압 약제의 수가 더 많았다. 치료 1년째 목표혈압 도달률은 고위험도군에서 유의하게 낮았다(고위험군 68.2%, 중등도위험군 85.2%, 저위험군 89.0%, p< 0.001). 당뇨병이나 신장 질환이 있는 환자들에서는 그렇지 않은 환자들에 비해 목표혈압 도달률이 더 낮았고(50.7% vs. 81.6%, p< 0.001) 목표혈압에 도달하기까지 걸린 시간도 더 길었다(106.5 ± 79.2일 vs. 82.1 ± 75.3일, p= 0.001). 다형회귀분석에서 고혈압 치료목표 달성 실패의 가장 중요한 결정인자는 치료 전 160 mmHg 이상의 수축기 혈압(위험비 [OR]: 4.91, 95% 신뢰구간 [CI]: 2.27~10.65), 동반된 신장 질환(OR: 3.43, 95% CI: 1.60~7.32), 중등도 이상의 WHO/ISH 위험도 군(OR: 2.27, 95% CI: 1.23~4.20), 치료 전 100 mmHg 이상의 확장기 혈압(OR: 2.11, 95% CI: 1.11~4.04), 그리고 동반된 당뇨병(OR: 2.06, 95% CI: 1.29~3.25)이었다.
Abstract
Background/Aims:
The aims of this study were to identify real world treatment patterns of hypertension according to cardiovascularrisk stratification and to evaluate blood pressure changes with anti-hypertensive treatment in each risk group.
Methods:
This study included patients who were newly-diagnosed with hypertension or known hypertensive patients withuncontrolled blood pressure (BP) at seven tertiary hospitals in Busan and Ulsan. World Health Organization/International Societyof Hypertension (WHO/ISH) cardiovascular risk stratification was performed through retrospective chart review.
Results:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were the most frequently prescribed drugs.The higher WHO/ISH risk group received a greater number of drugs at the initial treatment, and one year after treatment. Target BPwas achieved less frequently in the higher risk group (68.2% vs. 85.2% vs. 89.0%, p< 0.001). The rate of attaining target BP waslower (50.7% vs. 81.6%, p< 0.001), and the time to attaining target BP was longer (106.5 ± 79.2 days vs. 82.1 ± 75.3, p= 0.001), inpatients with renal disease or diabetes. Initial systolic BP above 160 mmHg (OR: 4.91, 95% CI: 2.27~10.65), renal disease (3.42,1.60~7.32), medium or high risk group status (2.27, 1.23~4.20), initial diastolic BP above 100 mmHg (2.11, 1.11~4.04), anddiabetes (2.06, 1.29~3.25) were independent factors that predicted failure of attaining the target BP.
고혈압은 만성질환 중 발생빈도가 매우 높은 질환으로 2002년 세계보건기구(World Health Organization, WHO) 보고에 의하면 전 세계 고혈압 유병인구는 10억이 넘고, 매년 7백만의 사람들이 고혈압으로 인해 사망하는 것으로 추정된다[1]. 우리나라에서도 고혈압은 만성질환 중 비만 다음으로 유병률이 높아 국민건강영양조사 제4기 1차년도인 2007년의 조사결과에 따르면 우리나라 만 30세 이상의 고혈압 유병률은 24.9%에 이르며, 연령이 증가할수록 유병률이 증가하는 것으로 알려져 있다. 우리나라는 2007년 전체 사망 중 8.8%가 심혈관 질환이 원인이 되며[2], 심혈관 질환으로 인한 국민건강보험 급여 지출은 전체 지출의 11%를 차지하고 있다[3]. 따라서 고혈압의 예방과 치료는 개인과 국가의 중요한 보건의료 문제가 되었다.
2007년 발표된 유럽 고혈압학회/유럽 심장학회 진료지침에서는 고혈압 환자의 심혈관 위험도를 평가할 때 이전보다 심혈관계 위험인자와 장기 손상의 범위를 더욱 확대시켰고, 대사증후군을 새로 포함시켰으며 특히 심혈관 질환 고위험군에 대한 고혈압 조절의 중요성을 강조하였다[4]. 또한 고혈압 치료 목표도 강화되어 당뇨병과 기존의 심혈관 질환을 가진 환자뿐만 아니라 심혈관 질환 고위험군과 초고위험군 환자도 130/80 mmHg 아래로 혈압을 조절할 것을 권고하고 있다. 미국 심장학회 역시 심혈관 질환 고위험군 환자와 허혈성 심장질환이 동반되어 있는 환자의 고혈압 치료목표를 이전보다 강화된 130/80 mmHg 미만으로 설정함으로써 환자 개개인에 대한 맞춤형 진료를 통해 보다 엄격한 혈압조절을 요구하고 있다[5]. 강화된 외국의 진료지침에 비추어 우리나라의 현실을 살펴보면 2007년 제4기 1차년도 국민건강영양조사에 의한 만 30세 이상 고혈압 인지율 63.5%, 치료율 54.8%, 조절률 38.0%로 1998년 인지율 24.6%, 치료율 21.9%, 조절률 5.1%에 비해 지난 10년간 지속적으로 개선되었다. 하지만 경제활동이 왕성한 30~40대의 고혈압 관리현황은 인지율 46.4%, 치료율 36.9%, 조절률 25.0%로 다른 연령대에 비해 가장 낮은 수준이었다. 따라서 심혈관 질환 발생으로 사회경제학적으로 많은 손실이 발생할 수 있는 30~40대의 고혈압을 철저히 관리하기 위해서는 우리나라 현실에 맞는 과학적인 전략 수립이 필요한 상태이다.
현재까지 고혈압 관리에 대한 많은 역학연구들이 있었으나 기존의 고혈압연구들은 일반 지역사회 고혈압 환자의 사회경제적 특성을 비교한 단면연구가 많았다. 그러나 실제 진료 현장에서 심혈관 위험인자에 따른 고혈압 치료 형태에 관련된 연구는 드물었다. 이에 본 연구에서는 부산, 울산 지역의 7개 종합병원을 방문하여 처음 고혈압 진단을 받은 환자에 대해 심혈관 위험도에 따라 대상 환자를 층별화 하고 진료 형태 및 혈압 변화를 후향적으로 분석하여 심혈관 위험도 별 고혈압 조절간의 상관관계를 알아보고자 하였다.
2007년 1월 2일부터 인제대학교 부산백병원, 부산대학교병원, 동아대학교병원, 고신대학교 복음병원, 울산대학교병원, 메리놀병원, 그리고 대동병원 심장내과를 방문하여 처음 고혈압을 진단받고 외래진료를 받은 20세 이상의 성인을 대상으로 하였다. 기존에 고혈압 약제를 복용하고 있었던 환자는 해당 병원 최초 진료 당시 혈압이 조절되지 않아 기존 약제에서 치료내용이 변경된 경우 연구대상에 포함하였다. 본 연구에 포함될 시점에 안정형 협심증, 급성 관동맥 증후군, 심부전증, 심장판막증을 동반한 경우는 그 치료약제가 혈압에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로 고혈압을 처음 진단 받아도 연구대상에서 제외하였다. 또한 이차성 고혈압, 기립성 저혈압, 심각한 심실성 부정맥 환자도 대상에서 제외하였다.
첫 방문 및 외래 경과관찰 때 안정한 상태에서 앉은 자세로 측정된 혈압과 맥박을 이용하였다. 본 연구 시작 전 치료가 되고 있던 환자는 병원의무기록을 조사하였으며 최초 처방 시점에서 가능한 1년 이상의 혈압과 맥박을 분석하였다. 치료 시작 후 1년째 측정된 혈압이 없으면 최초 처방 11월에서 13개월 사이에 측정된 혈압을 1년째 혈압으로 간주하였다. 입원하였던 환자의 경우 입원기간 중 혈압과 맥박 수치도 혈압변화의 분석 대상에 포함하였으며, 혈압을 측정할 때 사용한 혈압계의 종류는 구분하지 않았다.
미국이나 유럽인의 치료를 위해 제정된 미국 국립 보건원 산하 고혈압 합동 위원회 7차 보고서[6]나 2007년 유럽 고혈압학회/유럽 심장학회 기준[4]에 비해 각국의 고혈압 진료지침 개발 본보기의 목적으로 만들어져 2003년 개정된 세계 보건 기구/국제 고혈압학회(World Health Organization/International Society of Hypertension, WHO/ISH) 기준[7]에 따라 심혈관 위험도를 층별화하였다. 본 연구 시작 전 치료가 되고 있던 환자는 후향적으로 의무기록에 남아있는 자료를 분석하였고, 심혈관계 위험인자, 장기손상, 혈압과 관련된 임상상의 유무로 저위험군, 중등도위험군, 고위험군으로 나누었다. 대상 환자들 중 공복 혈당이 126 mg/dL 이상이거나 이미 경구 혈당강하제 또는 인슐린 치료를 받고 있는 경우는 당뇨병이 있는 것으로 간주하였고, WHO/ISH 기준에 따라 혈장 크레아티닌 수치가 남자 1.5 mg/dL, 여자 1.4 mg/dL를 초과하는 경우 또는 하루 300 mg을 초과하는 알부민뇨가 있는 경우 신장 질환이 있는 것으로 간주하였다.
항고혈압 약제를 안지오텐신 전환효소 억제제(angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ACE-I) 혹은 안지오텐신 II 수용체차단제(angiotensin receptor blocker, ARB), 베타차단제, 칼슘차단제(calcium channel blocker, CCB), 이뇨제, 그리고 기타 제제 다섯 가지로 구분하였다. 최초 사용한 항고혈압 약제의 종류와 개수, 목표 혈압 도달 기간, 목표 혈압에 도달했을 때의 항고혈압 약제의 종류와 개수를 분석하였다. 또한 목표 혈압에 도달하기 위해 사용한 항고혈압 약제의 종류나 용량의 변화가 있었는지 조사하였다. 최근 많이 사용되고 있는 두 가지 성분으로 구성된 복합제제를 복용하는 경우는 두 가지 약제를 복용하는 것으로 간주하였다. 항고혈압 약제 외에 항혈소판제와 고지혈증 약제 등의 투약 내용도 확인하였으며 항혈소판제와 고지혈증 약제의 종류는 구분하지 않았다.
환자 개개인에 대한 목표 혈압은 고혈압 합동 위원회 7차 보고서, 2007년 유럽 고혈압 학회/유럽 심장학회 및 WHO/ISH에서 제시하는 권고 사항을 참조하여 수축기혈압 140 mmHg 미만, 확장기혈압 90 mmHg 미만으로 하되, 당뇨병이나 신장질환을 동반한 경우는 수축기혈압 130 mmHg, 확장기혈압 80 mmHg 미만으로 정하였다.
연속형 변수는 평균 ± 표준편차로, 범주형 변수는 빈도 및 백분율로 나타내었다. 연속형 변수는 Student t-test 혹은 ANOVA 검사로, 범주형 변수는 Chi-square 혹은 Fisher’s exact test를 시행하여 WHO/ISH 기준에 따른 위험도와 당뇨병 및 신장 질환 유무에 따른 치료 형태 및 혈압 변화와의 관련성을 비교하였다. 당뇨병이나 신장 질환의 유무에 따른 목표혈압 도달기간의 차이는 Kaplan-Meier 및 Log-rank test를 이용하였으며, 치료 1년째 목표혈압 도달과 관련된 요인분석은 다형회귀분석을 이용하였다. p 값이 0.05 미만인 경우 통계학적인 의미를 두었다. 통계분석은 SAS 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA)를 이용하였다.
총 643명의 환자가 분석 대상에 포함되었고, 평균 452.32 ± 208.91일 동안의 자료를 분석하였다. 남자 321명(49.9%), 여자 322명(50.1%)으로 평균 나이는 56.7 ± 12.1세였다(Table 1). WHO/ISH 기준에 따른 심혈관 위험도는 저위험군 100명(15.6%), 중등도위험군 229명(35.6%), 고위험군 314명(48.8%)이었다. 심혈관 질환의 위험인자 대부분은 고위험군에서 빈도가 높았으나 고콜레스테롤혈증의 빈도는 통계적 유의성이 없었다. 고위험군 314명 중 당뇨병이 112명(35.7%), 허혈성 뇌졸중이 60명(19.1%)에서 동반되어 있었다. 처음 치료 때 항고혈압 약제는 전체 대상 환자 643명 중 45.3%가 단일 약제, 34.1%가 두 가지 약제, 20.6%가 세 가지 이상의 약제를 처방 받았다(Table 2). 단일 약제 처방은 저위험군에서 많았고, 세 가지 이상 약제 처방 빈도는 위험도 증가와 통계학적 관련이 없었다. 치료 1년째 단일 약제 처방은 저위험군에서 많았고 세 가지 이상 약제 처방 빈도는 위험도 증가에 따라 증가하였다.
최초 항고혈압 처방 약제 중에서는 ACE-I 또는 ARB (69.1%)와 CCB (58.5%)가 가장 빈번하게 처방되고 있었고, 이뇨제(29.2%)와 베타차단제(25.5%)는 비슷한 빈도로 처방되고 있었다(Fig. 1). 그 밖에 알파차단제와 질산염 제제가 소수(3.3%)에서 사용되고 있었다. 각각의 항고혈압 약제는 단일 약제 처방보다는 다른 종류의 약제와 같이 처방되는 경우가 많았으며, 특히 베타차단제와 이뇨제는 거의 대부분이 다른 종류의 약제와 같이 처방되고 있었다(Fig. 1). 처음 치료 시점과 비교하여 치료 1년째 모든 약제의 처방빈도가 증가되었다(Fig. 2). ACE-I 또는 ARB 처방빈도는 처음 치료시점과 치료 1년째 모두 위험도가 증가할수록 처방빈도가 증가되었으며, CCB와 베타차단제는 위험도 증가와 처방 빈도 사이의 상관관계는 없었다. 이뇨제 처방빈도는 처음 치료시점과 1년째 모두 고위험군에서 높았으나 통계적인 의미를 둘 수 없었다.
항고혈압 약제와 함께 처방되는 항혈소판 약제와 고지혈증 약제는 처음 치료시점과 치료 1년째 모두 특히 고위험군에서 처방 빈도가 높았고, 저위험군과 중등도위험군에서는 큰 차이가 없었다(Table 3).
전체 대상 환자 643명 중 치료 시작 후 1년 이내에 목표혈압에 도달한 사람은 498명(77.4%)이었다(Table 4). WHO/ISH 위험도가 증가할수록 목표혈압 도달 빈도가 의미있게 낮았으며, 목표혈압에 도달까지 더 오랜 기간이 소요되는 경향을 보였다. 전체 대상 환자 중 199명(41.5%)에서 항고혈압 약제 종류나 용량이 변경되었는데 동일한 약제의 용량을 증량했던 경우는 110명(17.1%)에 불과했고, 대부분 다른 종류의 항고혈압 약제를 기존 처방에 추가하거나 혹은 한 종류의 항고혈압 약제를 다른 종류의 항고혈압 약제로 바꾸는 경우가 많았다. 그러나 이러한 처방 형태는 각 위험도 군별로는 통계적 차이가 없었다(p= 0.120).
부산, 울산 지역 7개 종합병원에서 처음 고혈압을 진단 받은 환자의 치료 형태를 살펴본 본 연구에서 다음과 같은 몇 가지 사실을 확인하였다. 첫째, 전체 환자에서 ACE-I 또는 ARB와 CCB가 가장 빈번하게 처방되고 있었고, 각각의 항고혈압 약제는 단일 약제 처방보다는 다른 종류의 약제와 같이 처방되는 경우가 많았다. 둘째, WHO/ISH 심혈관 위험도가 높은 고혈압 환자일수록 처방 받은 항고혈압 약제의 수가 많았고, 위험도가 증가할수록 ACE-I 또는 ARB의 처방빈도가 증가하였다. 셋째, 모든 환자에서 목표혈압에 도달하기 위해 항고혈압 약제의 용량을 늘리기보다는 종류를 바꾸거나 다른 종류의 약제를 추가하는 경향이 있었다. 넷째, 치료 환자 중 74.7%가 치료 시작 후 1년 이내에 목표혈압에 도달하였으며 WHO/ISH 심혈관 위험도가 증가할수록 목표혈압 도달 빈도가 낮았다. 다섯째, 당뇨병이나 신장 질환이 있는 환자는 당뇨병이나 신장 질환이 없는 환자에 비해 치료 시작 후 1년 이내에 목표혈압에 도달한 빈도가 낮았으며 목표혈압 도달 환자의 목표혈압 도달기간도 더 길었다. 여섯째, 모든 환자에서 치료 시작 후 1년 이내 목표혈압 도달 실패를 예측할 수 있는 독립 인자는 치료 전 수축기 혈압 160 mmHg 이상, 신장질환, 중등도 이상의 WHO/ISH 위험도 군, 치료 전 이완기 혈압 100 mmHg 이상과 당뇨병이었다.
최근의 항고혈압 약제 처방의 경향을 반영하듯 ACE-I 또는 ARB의 처방 빈도가 가장 많았고, CCB가 두 번째로 많은 빈도를 차지하였다. 처방된 ACE-I 또는 ARB의 약 25.3%가 복합제제였다. 복합제제는 복용하는 약제의 개수를 줄일 수 있으므로 환자의 약물 순응도를 높일 수 있어 최근 그 사용 빈도가 증가하는 것으로 생각된다. 반면 베타차단제와 이뇨제는 단독 요법으로 처방되는 경우는 극히 드물었는데 이 또한 최근 항고혈압처방 경향을 반영하는 것으로 판단된다. 그러나 본 연구는 고혈압을 진단 받은 시점에서 안정형 협심증, 급성 관동맥 증후군, 심부전증, 심장판막증 등이 있었던 경우는 그 해당 질환으로 인해 항고혈압 약제 선택에 제한이 있을 수 있으므로 연구대상에서 제외하였기 때문에 전체 고혈압 환자의 치료 형태를 반영했다고 볼 수는 없고, 한정된 단순 고혈압 환자에 대한 항고혈압 약제 처방의 변화를 단편적으로 보여준 것이라 하겠다.
최근의 다양한 연구에서 당뇨병이 동반된 고혈압 환자 및 표적 장기 손상이 있는 고혈압 환자에게 항고혈압제로 ACE-I 또는 ARB를 권고하고 있다[8-11]. 본 연구에서도 이를 반영하듯 WHO/ISH 심혈관 위험도가 높은 고혈압 환자일수록 처방 받은 항고혈압 약제의 수가 많고 ACE-I 또는 ARB의 처방빈도가 증가하였다. 이는 WHO/ISH 심혈관 위험도 평가항목에 혈압수치가 포함되므로 WHO/ISH 위험도가 증가할수록 처음 치료시점에서 혈압이 높고, 당뇨병과 신장 질환이 많이 동반되었기 때문이라고 생각된다.
본 연구에 포함된 고혈압 환자의 대부분은 목표혈압에 도달하고 있었으나 WHO/ISH 위험도가 높은 환자와 당뇨병이나 신장 질환을 가진 환자, 그리고 처음 내원 시 확장기 혈압이 높았던 환자에서 혈압 조절이 잘 안되고 있었다. WHO/ISH 위험도가 높은 환자 및 당뇨병이나 신장 질환을 가진 환자가 항고혈압약제에 대한 치료효과가 낮다기보다는 처음 치료시점에서 WHO/ISH 위험도가 낮은 환자나 당뇨병, 신장 질환이 없는 환자와 비교해 혈압이 높기 때문이라고 판단된다. 최근 국내 1차 의료기관을 대상으로 한 고혈압 치료에 대한 Kim 등[12]의 단면 연구에서도 당뇨병(21.6%)이나 신장 질환(19.9%)이 있는 고혈압 환자의 혈압 조절률이 당뇨병이나 신장질환이 없는 환자(62%)에 비해 훨씬 낮다고 보고한 바 있다. 본 연구에 포함된 당뇨병이나 신장 질환 동반 고혈압 환자의 목표혈압 도달률(50.7%)이 Kim 등[12]의 연구에 비해 상대적으로 높은 것은 3차 의료기관과 1차 의료기관의 고혈압 치료형태의 차이 및 3차 의료기관에 내원한 고혈압 환자의 약물 순응도의 차이[13]가 중요한 원인이라고 생각된다. 다른 연구들에서도 본 연구결과와 비슷하게 혈압 조절 실패에 관계된 요인으로 표적 장기 손상과 동반 된 당뇨병이나 신장 질환을 꼽고 있다[14-16]. 본 연구에서 목표혈압으로 혈압을 조절 중 항고혈압 약제 변경은 박 등[17]의 연구에서와 마찬가지로 동일한 약제의 용량을 늘리는 경우는 매우 드물었고, 대부분 새로운 종류의 약제를 추가하여 항고혈압 약제의 개수를 늘리는 치료 형태를 보였다. 이러한 치료 형태는 각 위험도 군별로는 차이를 보이지 않았으며, 최대 용량의 항고혈압 약제에 따른 약제 부작용 등의 부담이 크게 작용한 것으로 추측된다. 또한 본 연구에 참여한 기관 및 의사가 한정적이었으므로 의사의 고혈압 관리에 대한 인식, 태도 및 처방 양상이 결과에 많은 영향을 미쳤을 수도 있다[18-20]. 혈압이 잘 조절되지 않는 고혈압 환자의 경우 최초 선택한 항고혈압 약제가 각 개인에 대한 고혈압의 병태 생리적 기전에 비추어 적절하지 못할 수도 있기 때문에[21,22], 서로 다른 종류의 항고혈압 약제를 같이 처방하는 것이 합리적일 수 있지만 한번에 복용해야 하는 약제의 개수가 늘어남에 따라 생길 수 있는 문제들도 고려할 필요가 있겠다.
목표혈압에 도달한 기간도 WHO/ISH 위험도가 증가할수록 그 기간이 더 긴 경향을 보였지만 통계적으로 의미를 둘 수 없었다. 그러나 당뇨병이나 신장 질환이 있는 환자는 없는 환자와 비교하여 목표혈압 도달기간이 통계적으로 유의하게 더 길었다. 목표혈압 도달 환자만 분석하면 치료 시작 후 3~4개월 동안 누적 목표혈압 도달 빈도의 격차가 벌어지다가 그 후부터 격차가 줄어드는 양상이었다. 이는 아마도 목표혈압에 제대로 이르지 못한 당뇨병 또는 신장 질환 환자에게 3~4개월 후부터 항고혈압 약제의 추가나 증량 등의 처방 변경이 있었기 때문으로 생각된다.
본 연구에서 심전도 혹은 심장초음파 검사는 93.3%의 환자에서 시행되었지만, 미세단백뇨 검사는 70.0%, 혈관 검사는 60.7%, 안저 검사는 42.3%에서 시행되었다. 많은 대상환자에서 표적장기의 손상 여부나 동반된 임상상의 평가를 후향적 의무자료 분석을 통해 시행하였고, 상당수 환자에서 동맥경화검사, 안저 검사 등이 실시되지 않았다. 따라서 본 연구대상 환자의 심혈관 위험도 층별화가 실제 위험도와 차이가 있을 수 있다. 참여 연구 기관이 지역의 대형 종합병원임을 생각할 때 표적 장기 손상 평가를 위한 노력이 부족한 것으로 생각된다. 이 연구는 지역 사회의 종합병원이라는 제한적 공간에서 비교적 단기간 동안 많지 않은 환자를 대상으로 실제 진료 현장의 치료형태를 보고자 한 후향적 연구이기 때문에 지역별 인구 구조의 차이를 감안하면[23,24] 우리나라 모든 고혈압 환자를 대변할 수는 없고, 혈압 조절 여부에 따른 임상상에 대한 추적 관찰이 부족하다. 또한 혈압 조절에 있어 항고혈압 약제와 함께 빼놓을 수 없는 생활 습관의 교정에 대해서는 본 연구에서는 확인할 수 없었다는 제한점이 있다. 그러나 본 연구의 결과는 앞으로 국내 고혈압 환자의 임상 연구를 진행함에 있어 연구 계획 단계의 참고 자료가 될 수 있을 것이고, 무엇보다 특히 고위험군 환자의 철저한 혈압 관리를 증진시키는 데 충분한 임상적 효용 가치가 있다고 생각한다. 이를 토대로 향후 더 많은 환자와 의사를 대상으로 한 범국가적 차원의 다기관 전향적 연구가 진행된다면 국내 고혈압 환자 치료의 유용한 지침으로 삼을 수 있을 것으로 사료된다.
REFERENCES
1. Guilbert JJ. The world health report 2002-reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Educ Health 2003;16:230.


2. 통계청편집부. 2007년 사망원인통계연보-전국편. 통계청. 2008.
3. 국민건강보험공단, 건강보험심사평가원. 2006 건강보험통계연보. 2007.
4. Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European society of hypertension (ESH) and of the European society of cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 2007;25:1105–1187.

5. Rosendorff C, Black HR, Cannon CP, et al. Treatment of hypertension in the prevention and management of ischemic heart disease: a scientific statement from the American heart association council for high blood pressure research and the councils on clinical cardiology and epidemiology and prevention. Circulation 2007;115:2761–2788.


6. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003;289:2560–2572.

7. Whitworth JA. 2003 world health organization (WHO)/international society of hypertension (ISH) statement on management of hypertension. J Hypertens 2003;21:1983–1992.


8. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet 2000;355:253–259.
9. Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1941–1951.


10. Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the losartan intervention for endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359:995–1003.

11. Lindholm LH, Ibsen H, Dahlöf B, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes in the losartan intervention for end-point reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359:1004–1010.

12. Kim KI, Kim Y, Kim HJ, et al. Current status and characteristics of hypertension treatment by primary physicians in Korea: data from Korean epidemiology study on hypertension (KEY study). Am J Hypertens 2008;21:884–889.


13. Sung J, Choi JH, On YK, et al. Study of compliance to antihypertensive medication in Korean hypertensive patients using medication event monitoring system. Korean Circ J 2005;35:821–826.
14. Banegas JR, Segura J, Ruilope LM, et al. Blood pressure control and physician management of hypertension in hospital hypertension units in Spain. Hypertension 2004;43:1338–1344.


15. Lloyd-Jones DM, Evans JC, Larson MG, O'Donnell CJ, Roccella EJ, Levy D. Differential control of systolic and diastolic blood pressure : factors associated with lack of blood pressure control in the community. Hypertension 2000;36:594–599.


16. Degli Esposti E, Di Martino M, Sturani A, et al. Risk factors for uncontrolled hypertension in Italy. J Hum Hypertens 2004;18:207–213.


18. Borzecki AM, Oliveria SA, Berlowitz DR. Barriers to hypertension control. Am Heart J 2005;149:785–794.


19. Pittrow D, Kirch W, Bramlage P, et al. Patterns of antihypertensive drug utilization in primary care. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2004;60:135–142.


20. Oliveria SA, Lapuerta P, McCarthy BD, L'ltalien GJ, Berlowitz DR, Asch SM. Physician-related barriers to the effective management of uncontrolled hypertension. Arch Intern Med 2002;162:413–420.


Prevalence of initial antihypertensive drugs use. Single denotes use of one antihypertensive drug and combination indicates use of more than two antihypertensive drugs. Twentyone patients who took an α-blocker or nitrates were not included in this analysis. ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; CCB, calcium-channel blocker.
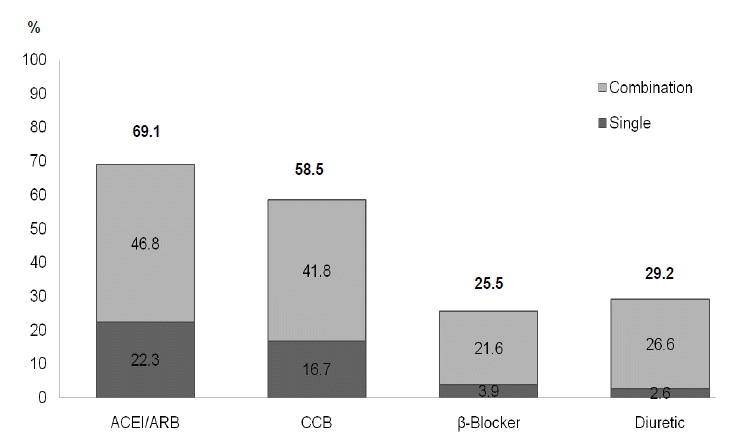
Figure 1.
Differences in the use of antihypertensive drugs according to WHO/ISH risk stratification at initial treatment and after 1 year of treatment. All types of drugs were increased after 1 year; ACEI/ARBs were prominently increased in the high risk group. ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; CCB, calcium-channel blocker.
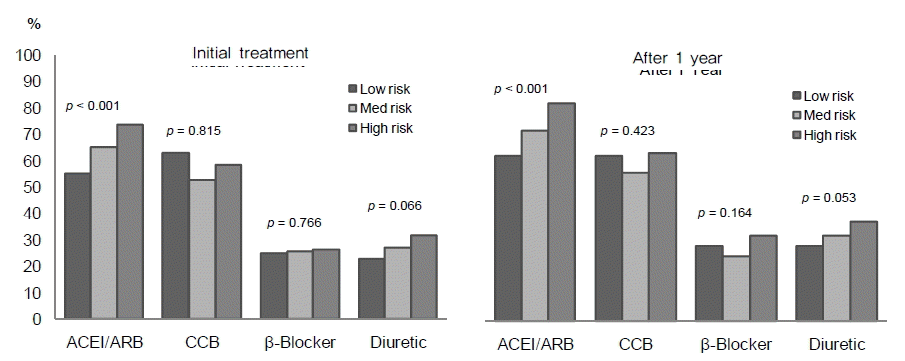
Figure 2.
Cumulative curve for achieving target blood in patients without DM or renal disease and with DM or renal disease. The rate of attaining target was lower in patients with diabetes or renal disease as compared to patients without diabetes or renal disease. DM, diabetes mellitus.

Figure 3.
Table 1.
Baseline clinical characteristics
|
WHO/ISH risk category |
p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Low risk (n = 100) |
Medium risk (n = 229) |
High risk (n = 314) |
||
| Age, yr | 51.3 ± 11.2 | 54.8 ± 11.2 | 59.1 ± 12.4 | <0.001 |
| Men, n (%) | 52 (52.0) | 104 (45.4) | 165 (52.5) | 0.235 |
| Cardiovascular risk factors, n (%) | 0.6 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Age above 55 or 65 yearsa) | 0 (0.0) | 86 (37.6) | 163 (51.9) | <0.001 |
| Smoking | 0 (0.0) | 43 (18.8) | 65 (22.9) | 0.021 |
| Hypercholesterolemiab) | 0 (0.0) | 34 (14.8) | 64 (20.4) | 0.072 |
| Low HDL cholesterolc) | 0 (0.0) | 42 (18.3) | 103 (32.8) | <0.001 |
| Family historyd) | 0 (0.0) | 73 (31.9) | 93 (29.6) | <0.001 |
| Obesitye) | 0 (0.0) | 16 (7.0) | 29 (9.2) | 0.006 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | ||||
| Diabetes | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 112 (35.7) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 60 (19.1) | <0.001 |
| Renal disease | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 32 (10.2) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.6) | 0.046 |
| Target organ damage, n (%) | ||||
| LVH | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 105 (33.4) | <0.001 |
| Microalbuminuria | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 76 (24) | <0.001 |
| Atherosclerotic plaque | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 22 (7.0) | 0.114 |
| Hypertensive retinopathy G-III/IV | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 21 (6.7) | 0.002 |
Table 2.
Number of anti-hypertensive drugs used at the initial treatment and after 1 year of treatment
Table 3.
Use of antiplatelet and cholesterol-lowering drugs at initial treatment and after 1 year of treatment
Table 4.
Differences in blood pressure control according to WHO/ISH risk stratification
Table 5.
Differences in blood pressure according to the presence of diabetes or renal disease
Table 6.
Factors associated with blood pressure control
| Controlled (n = 498) | Uncontrolled (n = 145) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men, n (%) | 244 (49.0) | 77 (53.1) | 0.384 |
| WHO/ISH risk | < 0.001 | ||
| Low | 89 (17.9) t | 11 (7.6) | |
| Intermediate | 195 (39.2) | 34 (23.4) | |
| High | 214 (43.0) | 100 (69.0) | |
| Initial SBP, mmHg | < 0.001 | ||
| Below 150 | 139 (27.9) | 11 (7.6) | |
| 151~159 | 176 (35.3) | 54 (37.2) | |
| Above 160 | 183 (36.7) | 80 (55.2) | |
| Initial DBP, mmHg | 0.003 | ||
| Below 95 | 319 (64.0) | 78 (53.8) | |
| 96~99 | 87 (17.5) | 20 (13.6) | |
| Above 100 | 92 (18.5) | 47 (32.1) | |
| Smoking, n (%) | 89 (17.9) | 26 (17.9) | 0.987 |
| Hypercholesterolemiaa), n (%) | 78 (15.7) | 20 (13.8) | 0.118 |
| Family history of CVDb), n (%) | 140 (28.1) | 26 (17.9) | 0.014 |
| Obesityc), n (%) | 39 (7.8) | 6 (4.1) | 0.125 |
| Diabetes | 69 (13.9) | 43 (29.7) | < 0.001 |
| CVD | 41 (8.2) | 19 (13.1) | 0.156 |
| Renal disease | 12 (2.4) | 20 (13.8) | < 0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.6) | 0.644 |
| No. of initial drugs, n (%) | 0.025 | ||
| Single | 239 (48.0) | 52 (35.9) | |
| Dual | 158 (31.7) | 61 (42.1) | |
| >Triple | 101 (20.3) | 32 (22.1) |
Table 7.
Independent predictors related to the failure to achieve target BP
- TOOLS
-
 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link XML Download
XML Download Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI-
 Download Citation
Download Citation
 Print
Print-
Share :








