ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļ│Ėļ¼Ė ļé┤ ņśżļźśĻ░Ć ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņłśņĀĢĒĢ®ļŗłļŗż.
ņØ┤ļōØņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ 10Ļ░£ņØś ļ¼┤ņ×æņ£ä ļīĆņĪ░ ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ņżæ 14Ļ░£ ļģ╝ļ¼Ė[4,6-18]ņØä
ņØ┤ļōØņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ 11Ļ░£ņØś ļ¼┤ņ×æņ£ä ļīĆņĪ░ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ņżæ 12Ļ░£ ļģ╝ļ¼Ė[4,6-16]ņØä
REFERENCES
1. Jin DC. Major changes and improvements of dialysis therapy in Korea: review of end-stage renal disease registry. Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:17-22.
2. Chen TK, Knicely DH, Grams ME. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: a review. JAMA 2019;322:1294-1304.
3. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117-2128.
4. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;380:347-357.
5. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:644-657.
6. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:323-334.
7. Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:369-384.
8. Del Prato S, Nauck M, Dur├Īn-Garcia S, et al. Long-term glycaemic response and tolerability of dapagliflozin versus a sulphonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 4-year data. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:581-590.
9. Haering HU, Merker L, Christiansen AV, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;110:82-90.
10. Hollander P, Hill J, Johnson J, et al. Results of VERTIS SU extension study: safety and efficacy of ertugliflozin treatment over 104 weeks compared to glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin. Curr Med Res Opin 2019;35:1335-1343.
11. Kaku K, Lee J, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease - results from EMPA-REG OUTCOME®. Circ J 2017;81:227-234.
12. Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W, List JF. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int 2014;85:962-971.
13. Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Merker L, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on therapy to pioglitazone with or without metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 2015;37:1773-1788.e1.
14. Merker L, H├żring HU, Christiansen AV, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in people with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 2015;32:1555-1567.
15. Ridderstr├źle M, Rosenstock J, Andersen KR, Woerle HJ, Salsali A; EMPA-REG H2H-SU trial investigators. Empagliflozin compared with glimepiride in metformintreated patients with type 2 diabetes: 208-week data from a masked randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:2768-2777.
16. Roden M, Merker L, Christiansen AV, et al. Safety, tolerability and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors of empagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind extension of a phase III randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2015;14:154.
17. Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Zeller C, et al. Impact of empagliflozin added on to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin: a 78-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:936-948.
18. Wilding JP, Woo V, Rohwedder K, Sugg J, Parikh S; Dapagliflozin 006 Study Group. Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin: efficacy and safety over 2 years. Diabetes Obes Metab 2014;16:124-136.
REFERENCES
1. Jin DC. Major changes and improvements of dialysis therapy in Korea: review of end-stage renal disease registry. Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:17-22.
2. Chen TK, Knicely DH, Grams ME. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: a review. JAMA 2019;322:1294-1304.
3. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117-2128.
4. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;380:347-357.
5. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:644-657.
6. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:323-334.
7. Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:369-384.
8. Haering HU, Merker L, Christiansen AV, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;110:82-90.
9. Kaku K, Lee J, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease - results from EMPA-REG OUTCOME®. Circ J 2017;81:227-234.
10. Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W, List JF. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int 2014;85:962-971.
11. Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Merker L, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on therapy to pioglitazone with or without metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 2015;37:1773-1788.e1.
12. Merker L, H├żring HU, Christiansen AV, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in people with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 2015;32:1555-1567.
13. Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Zeller C, et al. Impact of empagliflozin added on to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin: a 78-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:936-948.
14. Wilding JP, Woo V, Rohwedder K, Sugg J, Parikh S; Dapagliflozin 006 Study Group. Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin: efficacy and safety over 2 years. Diabetes Obes Metab 2014;16:124-136.
15. Bailey CJ, Gross JL, Hennicken D, et al. Dapagliflozin add-on to metformin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 102-week trial. BMC Medicine 2013;11:43.
16. Roden M, Merker L, Christiansen AV, et al. Safety, tolerability and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors of empagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind extension of a phase III randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2015;14:154.
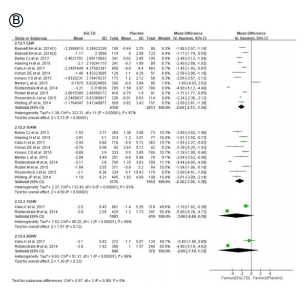
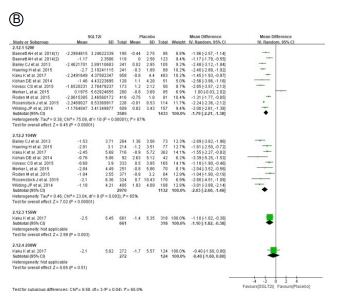
Figure 3. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on change of (A) HbA1c, (B) body weight, (C) systolic blood pressure, and (D) diastolic blood pressure. SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval.
Figure 3. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on change of (A) HbA1c, (B) body weight, (C) systolic blood pressure, and (D) diastolic blood pressure. SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval.
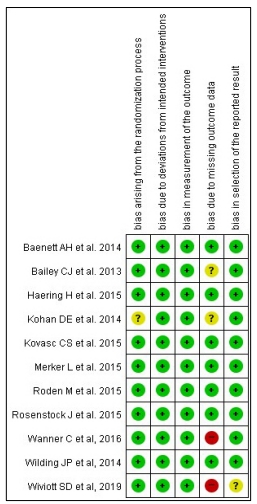
Supplementary fig. 1. Study quality and risk of bias assessment. The risk of bias of each randomized controlled trial was classified as adequate (low risk of bias, green color), unclear (unclear risk of bias, yellow color), or inadequate (high risk of bias, red color) using Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool.
Supplementary fig. 1. Study quality and risk of bias assessment. The risk of bias of each randomized controlled trial was classified as adequate (low risk of bias, green color), unclear (unclear risk of bias, yellow color), or inadequate (high risk of bias, red color) using Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool.